A few months ago, while having breakfast with colleagues, the conversation turned to how AI is reshaping work. Suddenly, someone asked a pivotal question: “How do you think the AI revolution is going to impact our planet? It consumes a massive amount of energy.”
It’s a valid concern. Companies, organizations, and nations feel forced to adopt AI to stay competitive, making its usage inevitable. While renewable options like solar and nuclear power exist, scaling them to meet this demand comes with significant challenges.
The Case for Local AI
Fortunately, there is a sustainable alternative. Many capable AI models designed for small-to-medium tasks can run directly on your personal computer. By shifting lighter workloads to local machines, we can collectively reduce the demand on massive, energy-intensive cloud infrastructure. It’s a win-win for productivity and the planet.
Beyond sustainability, running AI locally offers a major privacy advantage. You don’t have to worry about third-party companies collecting your personal data or injecting ads into your chat experience.
Previously, tools for running local models were often strictly command-line based and difficult to recommend to casual users. That has changed with Ollama.
Getting Started with Ollama
Ollama makes running these models incredibly user-friendly. Here is how to get set up:
- Download the App: Visit the Ollama download page to get the installer for your system.
- Install & Run: Once installed, Ollama typically downloads Google’s Gemma model by default. At around 3.3GB, it is efficient and runs smoothly on most modern computers.
Note: You can explore other models and check their file sizes in the Ollama Library.
The Experience
Ollama provides a clean desktop interface for chatting with your AI. For those who prefer it, the CLI (Command Line Interface) is also available and robust.
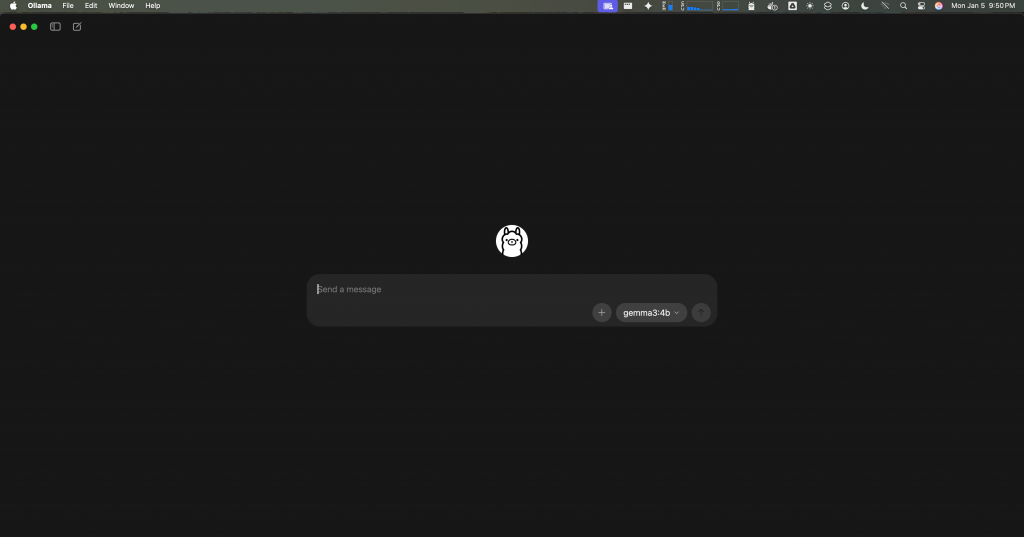
Here is a quick look at the CLI tool:
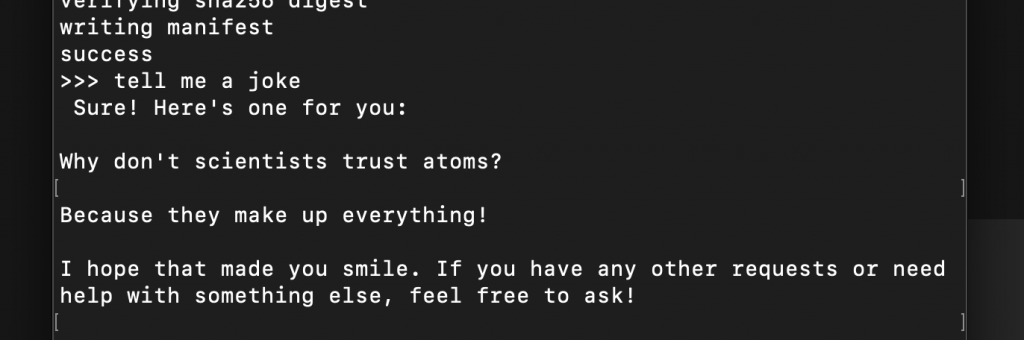
I guess the only real way to know you’re talking to an AI is that it always insists on having the last word! LOL.
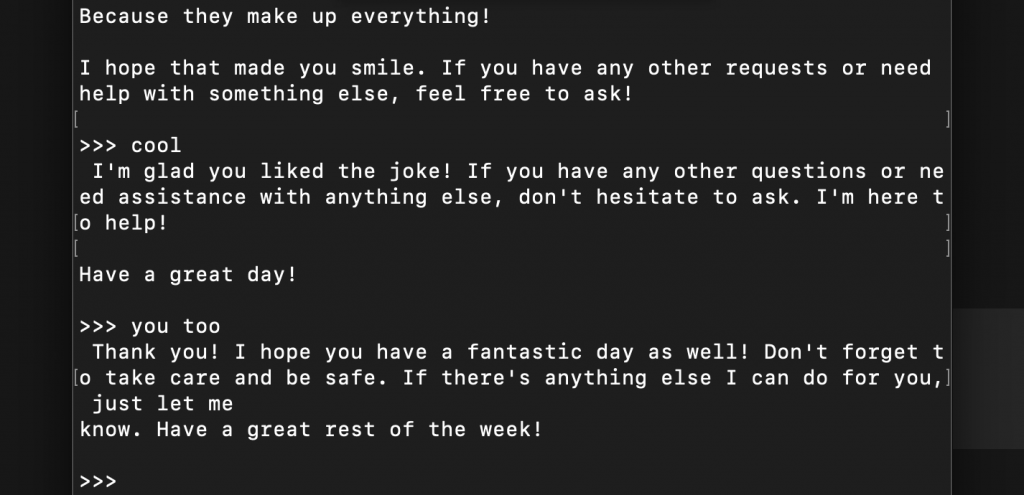
I have personally tested Mistral AI’s Mistral 7B and Meta’s Llama 3.2 on a Mac Mini M1 with 16GB of unified memory, and both performed very well.
Local AI is no longer just for developers. It is an accessible, private, cost-friendly and efficient way to use AI every day.